IL-7 is a hematopoietic growth factor that mainly affects early-stage B and T cells. IL-7 is generated by thymic stromal cells, splenocytes and keratin-forming cells, and can also jointly stimulate the proliferation of mature T cells together with other factors such as ConA and IL-2. IL-7 was originally considered a stroma-derived cytokine which can induce the growth of pre-B cells in vitro, and IL-7 acts through its receptor (IL-7R) on a variety of cells.
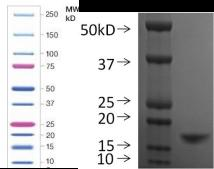
SDS-PAGE:
Biological Activity:
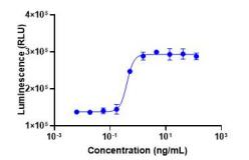
Measured by its ability to stimulate proliferation of PHA-activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC).The specific activity of recombinant Human IL-7 is ≥ 1.0 ×10^7 units/mg.
carrier proteins (such as 0.1% BSA, 10% FBS, and 5% HSA).
Order Imformations:
Cat.NO. Name Grade Size CY022F0010 IL-7 RUO 10 μg CY022F0020 IL-7 RUO 20 μg CY022F0050 IL-7 RUO 50 μg CYG022F0050 IL-7 GMP 50 μg CYG022F0500 IL-7 GMP 500 μg
Q:What are cytokines?
A:Cytokines (CK) are small molecule peptides or glycoproteins synthesized and secreted by various tissue cells (mainly immune cells). Cytokines can mediate interactions between cells and have various biological functions, such as regulating cell growth, differentiation and maturation, maintaining function, regulating immune response, participating in inflammatory response, wound healing, and tumor growth and decline.
Q: Common cytokines and their functions
A:(1) Interleukin (IL): A cytokine produced by lymphocytes, monocytes, or other non monocytes, playing an important regulatory role in intercellular interactions, immune regulation, hematopoiesis, and inflammatory processes.
(2) Colony stimulating factor (CSF): According to different cytokines, hematopoietic stem cells or hematopoietic cells at different stages of differentiation are stimulated to form different cell colonies in semi solid culture medium. Different CSFs not only stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells and progenitor cells at different developmental stages, but also promote the function of mature cells.
(3) Interferon (IFN) has essentially the same biological activity as various IFNs, and has antiviral, anti-tumor, and immunomodulatory effects.
Q: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)?
A:The basic biological activities of two types of TNF are similar. In addition to killing tumor cells, they also have immune regulation and participate in the occurrence of fever and inflammation. High dose TNF- α can cause cachexia, thus TNF- α Also known as cachectin.Q:Precautions for using cytokine freeze-dried products
A:During transportation, freeze-dried powder products may have powder adhering to the tube wall or cover. Before use, do not open the cover and centrifuge for 20-30 seconds (high-speed centrifuge, approximately 13000 rpm) to collect the protein attached to the tube cover or wall at the bottom of the tube. Using a centrifuge with a maximum speed of 4000-4500rpm for 5 minutes (3000-3500rpm) can also achieve a similar effect. Although sometimes the protein powder in the tube is not visible or the visible quantity is small, our quality control system ensures that the protein content in each tube is accurate and sufficient.
Q:Dissolution of cytokine freeze-dried products
A:(1) Preparation before use: Centrifuge before use (see above) to allow the protein attached to the tube cover or wall to settle at the bottom of the tube;
(2) Dissolved solution
① Require products to be dissolved in sterile deionized water. Be sure not to use salt solution to avoid irreversible protein precipitation caused by excessive salt concentration; Do not dissolve directly in PBS or culture medium (1640 or DMEM, etc.), otherwise the protein may not be fully dissolved, resulting in insufficient or inactivated protein activity;
② For products that require dissolution with salt solution, please follow the concentration specified in the instruction manual to avoid excessive salt concentration;
③ You can also contact our technical support for the selection of a solution for individual products.
(3) Dissolve to the specified concentration:
① We suggest that the optimal concentration should generally not be less than 100 μg/mL, such as 10 μg of freeze-dried powder, add 10 μL-100 μl Solution;
② Above or below the optimal concentration, cytokines may become unstable or aggregate, leading to partial protein precipitation and affecting their activity.
③ Use a pipette gun to gently blow and mix, or cover the tube cover and gently invert it several times to mix, centrifuge at low speed for a few seconds; Do not oscillate during dissolution to avoid protein inactivation caused by chemical bond breakage;
④ Leave the dissolved protein at room temperature for a few minutes to ensure full protein dissolution. It is recommended to use a low-speed shaking table to promote the dissolution of proteins that are not easily soluble.
(4) Storage after dissolution:
Further dilution with dissolved solution is not recommended. The protein in the solution is easily adhered to the frozen tube wall and difficult to separate from the tube wall. Use a solution containing carrier protein (usually a buffer with a pH close to neutral and a certain buffering capacity, such as PBS, culture medium, etc.) to pre seal the protein binding sites on the plastic tube wall, so that cytokines or recombinant proteins do not adhere to the tube wall, in order to better preserve the protein solution;
① Short term preservation: In general, the concentration recommended in the previous text is relatively high. We suggest diluting this solution with a solution containing carrier proteins (such as 0.1% BSA, 10% FBS, 5% HSA), sub packaging at 4 ℃, and using it within a week. The sub packaging volume should not be less than 20 μ L. Otherwise, diluted cytokines or recombinant proteins can easily adhere to the wall of the tube or bottle, causing a decrease in the concentration of cytokines or recombinant proteins in the solution, thereby affecting their biological activity;
② Long term storage: If the prepared solution cannot be used up at once, we suggest further diluting it with a solution containing carrier proteins (such as 0.1% BSA, 10% FBS, and 5% HSA), and freezing it in sub packages at -20 ℃ to -80 ℃. The sub package volume should not be less than 20 μ L;
③ When conducting serum-free culture or in vivo animal experiments, cytokines should not contain animal or human components such as BSA, FBS, or HSA. A solution containing 5% trehalose can be used to dilute the dissolved cytokines or recombinant proteins, and then packaged and frozen for storage, with a packaging volume not less than 20 μ L.
Q:What are the tests for recombinant proteins?
A:Gene sequence: Through N-terminal sequence analysis. If necessary, use methods such as SDS-PAGE, HPLC, and mass spectrometry to compare with standards;
Protein purity:
(1) Through SDS-PAGE
(2) HPLC Analysis
Biological activity: After relevant in vitro or in vivo biological activity testing, please refer to the following text for details;
Protein content:
(1) UV spectrophotometry
(2) Quantitative determination of BCA protein
(3) SDS-PAGE Analysis
(4) Comparison between HPLC method and standard substance
Endotoxin content: determined by dynamic LAL (Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate) method or TAL (Tachypleus Amebocyte Lysate) method;
Sterile: All protein solutions undergo 0.22 cycles before packaging and freeze-drying μ M filter membrane filtration for sterilization, packaging, freeze-drying, and sealing in B+A level environments;
Molecular weight: SDS-PAGE analysis;
Host protein residue: fluorescence staining;
Host DNA residue: ELISA kit;
Mycoplasma detection: Mycoplasma test kit.
Q: What is the biological activity of recombinant proteins?
A:The biological activity of proteins is a manifestation of various protein functions. Alternatively, you can understand that only proteins have activity can they perform their functions. Proteins with biological activity are called active proteins. In theory, natural proteins are all active proteins, while recombinant proteins are not always active proteins, as the production of recombinant proteins is a complex process in which many factors are crucial for their biological activity, such as ideal expression systems, suitable expression vectors, purification, etc.
1. Calculation of ED50:
The protein product ED50 (i.e. half effective concentration, defined as the protein concentration that causes a maximum response of 50% to a specific cell, in ng/mL) can be obtained in the protein product COA. This activity representation method is only applicable to cytokines with an S-shaped dose-response curve. If 1 ng/mL ED50 is defined as 1 unit, the conversion formula for the specific activity of the product's biological activity is as follows:
Specific Activity(units/mg)= 1 × 10 6 ÷ ED50(ng/mL)
The above calculation formula is not applicable to the conversion relationship between International Units (IU) and ED50. We suggest using international standards to compare the same experiment to obtain the IU value of this protein.
2. Factors affecting ED50:
The experimental plan in the product manual only confirms the ED50 of the product. If the customer's experimental type is the same as ours, they can conduct experiments according to the biological activity calibrated by the product; If different cell types or methods are used in the experiment, we suggest that the customer obtain the optimal ED50 value through the experiment according to the gradient concentration, and develop the corresponding experimental plan and product addition amount based on this value. If you have any questions about biological activity or experimental methods, you can contact our technical support (technical support: emailsupport@chaselection.com)